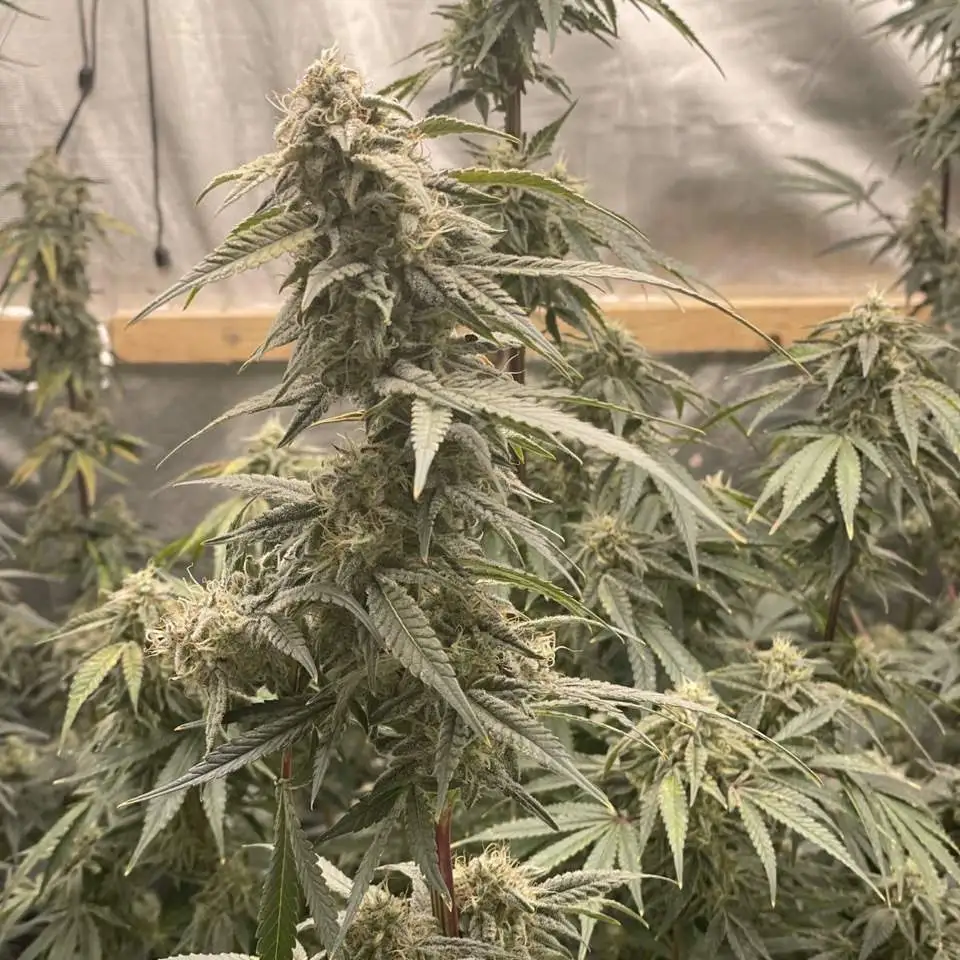
Great White Shark strain is a well-known cannabis strain that offers an appealing balance of effects, making it highly popular among both novice and experienced growers. A hybrid with a predominantly Indica profile, Great White Shark delivers a relaxing and euphoric experience that users often describe as both mentally uplifting and physically soothing. The strain is celebrated for its high resin production, making it ideal for those looking to produce concentrates and extracts. Its strong genetic lineage, a mix of Super Skunk, Brazilian, and South Indian strains, makes Great White Shark a potent cultivar with notable qualities.
Visually, Great White Shark presents dense, frosty buds covered in a thick layer of trichomes that sparkle like the teeth of its oceanic namesake. Its terpene profile is complex and alluring, with earthy and citrus notes complemented by hints of sweetness. This aromatic combination makes it a favorite for users seeking both recreational and medicinal benefits. With THC levels often reaching up to 20%, Great White Shark offers a powerful effect that helps with pain relief, stress reduction, and improving overall mood.
Environmental Requirements for Growing Great White Shark Strain
Growing Great White Shark Strain requires a specific set of environmental conditions to thrive. It’s a hardy strain that does well both indoors and outdoors, but providing the right conditions will significantly enhance the plant’s performance. Ideally, it grows best in a warm, Mediterranean-like climate if cultivated outdoors. The temperature should range between 70-85°F, with consistent sunlight to promote healthy growth and bud development.
Humidity control is crucial for it especially during its flowering phase. Maintaining humidity levels between 40% and 50% helps prevent mold and mildew, which can be problematic due to the dense structure of the buds. When grown indoors, controlling airflow with fans and dehumidifiers can make a big difference, particularly during the flowering stage. Outdoor growers should monitor weather forecasts closely to protect plants from sudden changes in humidity or unexpected rainfall.
Setting Up The Growing Cannabis Space
Whether you choose to grow it indoors or outdoors, setting up an effective grow space is key to success. For indoor setups, consider using grow tents to maintain full control over the plant’s environment. A grow tent allows you to regulate light, temperature, humidity, and airflow. Reflective materials within the tent maximize light efficiency, ensuring that your plants receive adequate exposure for optimal growth.
For outdoor cultivation, selecting the right location is critical. Choose a site that receives plenty of sunlight while providing some protection against strong winds. Using raised garden beds or large pots can help improve drainage, which is important to prevent root rot. Outdoor growers can also benefit from using organic soil rich in nutrients to give their plants the best possible start.
Indoor Cannabis Cultivation
Growing Great White Shark strain indoors offers growers complete control over the plant’s conditions, leading to higher yields and better-quality buds. Lighting is a significant factor in indoor cultivation. LED grow lights are recommended for their energy efficiency and ability to provide the full spectrum of light required during the different growth stages. Ensure your plants get at least 18 hours of light per day during the vegetative phase, dropping to 12 hours during the flowering phase to trigger bud production.
Indoor growers should also pay close attention to the growing medium. It performs well in hydroponic systems as well as soil. Hydroponics can accelerate growth and increase yields, but soil-grown plants often produce richer flavors due to the organic interactions between the plant and soil. Either way, monitoring pH levels is essential to ensure that the nutrients are effectively absorbed.
Outdoor Cannabis Cultivation
Cultivating it outdoors is ideal for growers who have access to a sunny and warm environment. Outdoor cultivation allows the plant to grow to its full potential, often resulting in larger yields compared to indoor grows. The key to a successful outdoor grow is timing, plant Great White Shark strain after the last frost has passed and ensure it has enough time to grow before temperatures start to drop in the fall.
Protecting outdoor plants from pests and environmental stressors is an important consideration. Natural pest repellents like neem oil can help keep insects away without the use of harsh chemicals. Also, consider staking the plants to support their branches as they grow heavy with dense buds. A good outdoor grow can produce exceptionally potent flowers that are rich in terpenes and cannabinoids.
Propagation and Germination
Propagation is the initial step to ensure a healthy cannabis crop. For Great White Shark strain, starting with high-quality seeds or clones is crucial. Seeds should be germinated using the paper towel method or directly in a rooting medium to promote healthy taproot development. This strain typically takes 3-5 days to germinate, and maintaining a warm and dark environment during this phase is key.
Once germinated, transfer the seedlings to small pots with nutrient-rich soil. It’s important to provide gentle lighting during this early stage to prevent shock. The seedlings will spend their first couple of weeks establishing a root system before they are ready to move on to the vegetative stage. During propagation, maintaining a humidity level around 60-70% helps keep the seedlings healthy.
Vegetative Phase of Great White Shark Strain
The vegetative phase is when Great White Shark establishes its structure, developing sturdy branches and a healthy root system. During this stage, it is vital to provide ample nitrogen to support growth. Growers should use a nutrient formula that promotes foliage development. This phase typically lasts 4-6 weeks, depending on the growing conditions and the desired plant size.
Ensure that Great White Shark gets sufficient light during the vegetative stage. Indoor growers should keep lights on for 18-20 hours a day, while outdoor growers should aim for maximum exposure to natural sunlight. Regular pruning and topping are recommended to encourage lateral growth, resulting in more bud sites and ultimately leading to higher yields.
Flowering Phase of Great White Shark
The flowering phase is where Great White Shark strain truly begins to shine. This phase typically lasts between 8-10 weeks, during which the plant develops dense, resinous buds. Reducing the light cycle to 12 hours triggers flowering for indoor growers, while outdoor plants begin to flower naturally as the days shorten towards the end of summer.
During flowering, phosphorus and potassium become more important nutrients. These nutrients help with bud development and resin production. It’s crucial to keep humidity levels low (around 40%) to prevent mold, especially since Great White Shark buds are dense and susceptible to moisture-related issues. The use of a bloom booster can also enhance flower production and potency.
Cannabis Fertilization and Nutrition
Feeding Great White Shark strain with the right nutrients is essential for a successful grow. During the vegetative stage, use fertilizers rich in nitrogen to encourage robust leaf growth. As the plant transitions into flowering, shift to nutrients higher in phosphorus and potassium to support bud development.
Organic options like compost tea or fish emulsion are great for those looking to grow in a more natural way. Monitoring pH levels ensures that nutrients are being absorbed efficiently, keep pH between 6.0 and 6.5 for soil and slightly lower for hydroponic systems. Over-fertilization should be avoided, as it can lead to nutrient burn, which will affect the quality of the final harvest.
Pest and Disease Control for Cannabis Growing
Prevention
Preventing pests and diseases is always preferable to treating an infestation once it occurs. For Great White Shark, maintaining a clean growing environment is crucial. Regularly inspect plants for early signs of pests like spider mites or aphids. Utilizing natural deterrents such as neem oil or introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs can help keep harmful pests at bay.
Another effective prevention strategy is to control humidity and airflow. Mold and mildew are common problems for cannabis plants, especially for strains like Great White Shark with dense buds. Ensuring proper ventilation and reducing excess moisture can significantly lower the risk of these issues.
Corrective Actions
If pests or diseases do manage to find their way to your plants, acting swiftly is essential. For minor pest issues, insecticidal soaps or neem oil can be effective. In cases of mold or mildew, pruning affected areas and adjusting environmental conditions to reduce humidity can help manage the spread. Always monitor the plants closely to ensure the problem is resolved and doesn’t recur.
Harvesting and Curing for Cannabis Growing
Harvesting Great White Shark strain at the right time is key to achieving the best potency and flavor. Look for the trichomes to turn milky white, with some amber heads, which indicates peak ripeness. Once harvested, trim the buds and hang them in a dark, well-ventilated space to dry for 7-10 days.
After drying, curing the buds in glass jars for at least two weeks will improve both flavor and potency. Open the jars daily for the first week to allow moisture to escape, then gradually reduce the frequency. Proper curing can make a significant difference in the overall quality.
Is Great White Shark Strain Indica or Sativa?
It is an Indica-dominant hybrid, known for its relaxing and calming effects. While it does contain some Sativa genetics, which contribute to a mildly uplifting cerebral high, the Indica influence is more pronounced, leading to full-body relaxation. This makes it ideal for evening use or for those seeking relief from pain and stress.
Advantages of Growing Great White Shark
One of the biggest advantages of growing Great White Shark is its resilience. It is a hardy plant that can withstand common stressors, making it suitable for growers of all skill levels. Additionally, its high resin production makes it perfect for those interested in creating concentrates or hash.
It also offers a relatively short flowering period of 8-10 weeks, which is advantageous for those looking to harvest multiple times a year. Its dense buds and strong terpene profile make it a rewarding strain to grow, both in terms of yield and quality.
Disadvantages of Growing Great White Shark
Despite its many advantages, there are some challenges to growing it. Its dense buds make it susceptible to mold, especially in high-humidity environments. This requires growers to be vigilant about humidity control, particularly during the flowering phase.
Another potential downside is the strong odor produced by Great White Shark strain during flowering. While this is a positive for many due to its enticing aroma, it can be problematic for those needing to maintain a discreet grow. Utilizing carbon filters can help manage the smell in indoor grow spaces.
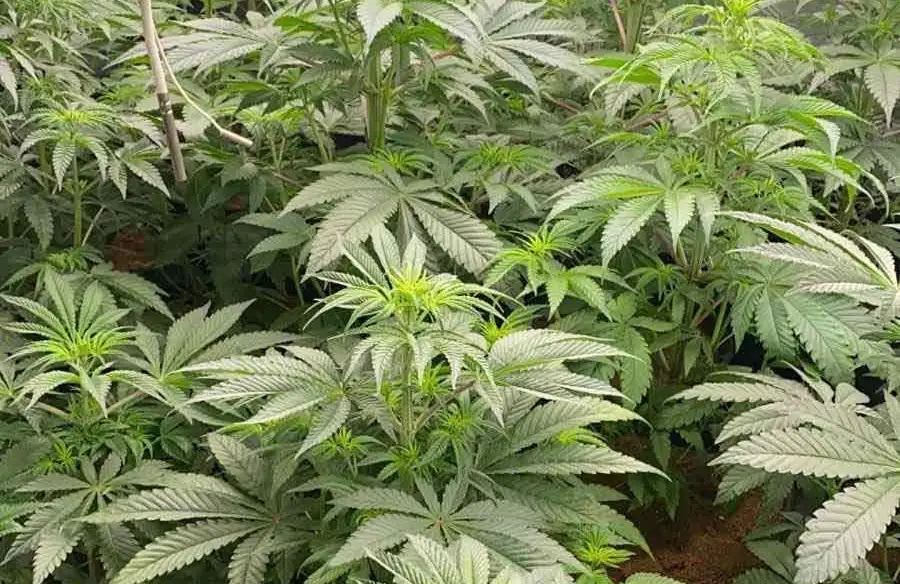

Problems in Cultivating Great White Shark strain
One common problem in cultivating it is over-fertilization. This strain can be sensitive to excessive nutrients, particularly during the early stages of growth. It’s important to start with a lower dose of nutrients and gradually increase as the plant shows signs of needing more.
Another issue growers may face is pest infestations, particularly spider mites and aphids. Regular monitoring and early intervention are key to preventing these pests from becoming a major problem. Using natural pest repellents and keeping the grow space clean can significantly reduce the risk of infestations.
Advanced Pest Control for Cannabis Growing
For those dealing with persistent pest problems, advanced pest control techniques may be necessary. Introducing predatory insects like ladybugs or lacewings can help keep pest populations under control. Additionally, using horticultural oils and biological fungicides can provide an extra layer of defense without harming the plants.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is another effective strategy, combining cultural, biological, and chemical controls to keep pests at bay. Regular monitoring and a proactive approach are essential components of an IPM plan, particularly for a strain like Great White Shark strain that can be susceptible to certain pests.
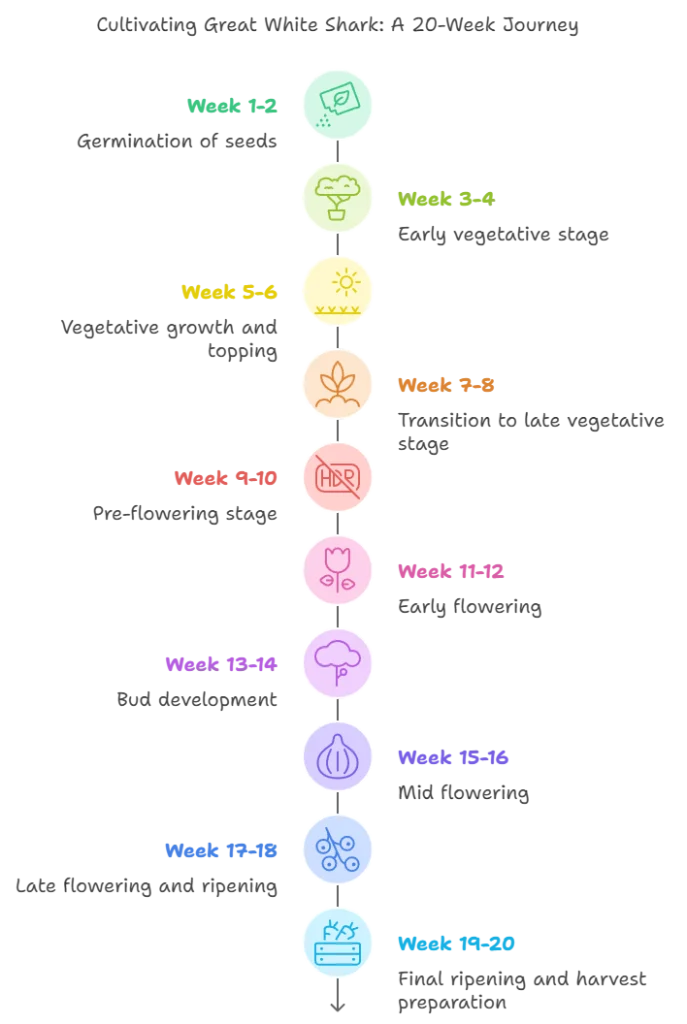
Week-by-Week Growth Plan
Week 1-2: Germination
In the first two weeks, focus on germinating the Great White Shark seeds. Keep them in a warm, moist environment, either using the paper towel method or directly planting them in soil. Ensure temperatures remain between 70-75°F for optimal results. Once germinated, seedlings need gentle light and stable humidity to thrive. Provide a small grow light or fluorescent bulb to give consistent illumination for 18-24 hours a day.
Week 3-4: Early Vegetative Stage
During these weeks, transplant the seedlings into larger pots. Provide 18-20 hours of light daily, and begin a mild nutrient regimen high in nitrogen to promote healthy leaf growth. Keep an eye on temperature and humidity levels, aiming for 50-60% humidity and temperatures between 70-80°F. Water regularly, but avoid overwatering as young roots are still delicate. Monitor the plants for healthy leaf development and ensure they receive adequate airflow.
Week 5-6: Vegetative Growth and Topping
The vegetative stage continues, with the plants needing more space to grow. Transplant into larger pots if needed. During this period, topping can be performed to encourage more lateral growth, which leads to increased bud sites. Prune lower leaves to allow light penetration and improve airflow. Increase the strength of nutrients slightly, maintaining a focus on nitrogen-rich formulas. Humidity levels can be reduced to 50% as the plants grow sturdier.
Week 7-8: Transition to Late Vegetative Stage
The plants will continue to grow vigorously during weeks 7 and 8. Continue providing 18-20 hours of light daily. At this point, plants may require additional support to ensure branches grow strong enough to hold the weight of future buds. Introduce silica supplements to help strengthen cell walls and boost plant health. It’s also a good time to start monitoring for any signs of pests or nutrient deficiencies.
Week 9-10: Pre-Flowering Stage
As Great White Shark transitions into the flowering stage, change the light schedule to 12 hours on and 12 hours off to trigger the flowering response. This is called the pre-flowering stage, where plants stretch in size and prepare to develop buds. Reduce the nitrogen in your nutrient mix and begin adding more phosphorus and potassium to support the upcoming bud production. Aim for humidity levels around 45-50% and keep airflow strong to prevent moisture buildup.
Week 11-12: Early Flowering
During early flowering, the first pistils (white hairs) will begin to appear, indicating bud sites. Maintain the 12/12 light schedule, and adjust nutrients to a flowering blend, focusing on phosphorus and potassium. Keep humidity levels between 40-45% to reduce the risk of mold, as the buds begin to develop and compact. Monitor for pests and nutrient deficiencies, as any issues should be caught early for best results.
Week 13-14: Bud Development
Bud development intensifies during weeks 13 and 14. The plants will now be focused on producing dense flowers, and you will start to notice the buds gaining size and structure. Feeding should continue with bloom-boosting nutrients, which are high in phosphorus and potassium. Consider adding a bloom enhancer for an extra boost. Maintain humidity at 40% and ensure plenty of airflow around the buds to prevent any moisture issues.
Week 15-16: Mid Flowering
By this stage, buds are visibly swelling and the aroma will become stronger. Continue with the flowering nutrients, and consider adding molasses or other carbohydrate supplements to enhance terpene and resin production. Ensure light penetration is maximized by gently moving any large fan leaves blocking bud sites. The environment should stay stable, with temperature between 70-75°F and humidity around 35-40%.
Week 17-18: Late Flowering and Ripening
Late flowering is when the buds begin to ripen and reach their full potency. Keep the environment consistent, but reduce nutrient feeding and begin flushing with plain water to remove any built-up salts and chemicals from the growing medium. This ensures a cleaner, smoother final product. Look for signs of trichome maturity, cloudy or amber trichomes are a sign that harvest time is approaching. Keep humidity low, around 30-35%, to avoid any mold development.
Week 19-20: Final Ripening and Harvest Preparation
In the final two weeks, focus on flushing and preparing for harvest. Reduce light intensity slightly to mimic natural conditions as autumn approaches, which can also help stimulate more resin production. Trichomes should be monitored daily to determine the optimal time for harvest. When most trichomes are milky with some amber, it’s time to cut. Ensure all tools are clean, and prepare a dark, well-ventilated area for drying.
FAQs
What is the THC percentage of Great White Shark Strain?
It typically has THC levels ranging between 15% and 20%, depending on growing conditions and phenotypes.
How long does it take for Great White Shark strain to flower?
The flowering period for this strain is usually between 8-10 weeks.
What flavors and terpenes are present in Great White Shark strain?
It has a rich terpene profile that includes earthy, citrus, and sweet notes, with prominent terpenes like myrcene, limonene, and caryophyllene.
Can Great White Shark strain be grown both indoors and outdoors?
Yes, it is versatile and can be successfully grown both indoors and outdoors, provided the right environmental conditions are met.
What are the medicinal benefits of Great White Shark?
It is often used for pain relief, stress reduction, and to help with insomnia due to its relaxing and calming effects.